


Next: Connection Teardown
Up: The Distributed Admission Control
Previous: The Distributed Admission Control
An application seeking to establish a connection contacts the local
HEC, which in turn initiates a three-pass
connection establishment procedure. Although we limit ourselves
to a source-initiated,
source-routed scenario, this scheme can be adapted to
destination-initiated or adaptive routing schemes as well. In the following,
we briefly describe the procedure. For a more detailed description, please
refer to [12].
Pass 1
The HEC at the sender host sends an establish request message,
which travels downstream to the destination processed by each SEC along the
route. The establish request message for the new
connection 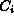 contains the worst-case message length of Connection
contains the worst-case message length of Connection 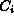 and information about connections that branch in at switches upstream.
This information, which is updated by each SEC along the path, is used in
Pass 2 to calculate the BI and BO values defined in
Section 3.
and information about connections that branch in at switches upstream.
This information, which is updated by each SEC along the path, is used in
Pass 2 to calculate the BI and BO values defined in
Section 3.
Pass 2
When the establish request message reaches the destination host, the
second pass is invoked by sending an establish reply message
upstream to the sender host. As the message is sent from 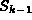 to
to
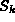 , it contains the value
, it contains the value 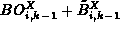 . This value
is zero when the message is sent from the destination host to the next
switch upstream.
Upon receiving an establish reply message for
. This value
is zero when the message is sent from the destination host to the next
switch upstream.
Upon receiving an establish reply message for 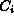 from
from
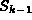 , the local SEC at
, the local SEC at 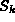 calculates the local value of
calculates the local value of 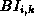 and can now
determine the guard-based calculated worst-case blocking delay
and can now
determine the guard-based calculated worst-case blocking delay
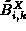 . It then checks whether
. It then checks whether 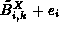 is
less than or equal to the local blocking guard,
is
less than or equal to the local blocking guard, 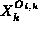 and
aborts the establishment process if not. Otherwise it continues the process
by locally computing
and
aborts the establishment process if not. Otherwise it continues the process
by locally computing 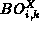 and forwarding
and forwarding 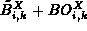 to the next SEC upstream.
to the next SEC upstream.
Pass 3
When the establish reply message reaches the HEC at the source
host, the final acceptance test is performed by comparing the
value in the establish reply with the deadline requirements of 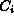 .
If the test fails, the connection is rejected and the establishment procedure
aborted. Otherwise, the third and final pass is invoked by sending an
establish confirm message along the route of
.
If the test fails, the connection is rejected and the establishment procedure
aborted. Otherwise, the third and final pass is invoked by sending an
establish confirm message along the route of 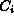 to the
destination host. When sent from
to the
destination host. When sent from 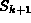 to
to 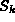 , this message
contains the entry
, this message
contains the entry 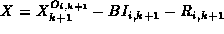 and
the number of hops to the destination, k.
The initial value of X at the sender HEC is
and
the number of hops to the destination, k.
The initial value of X at the sender HEC is 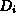 .
Upon receiving an establish confirm message, the SEC at
.
Upon receiving an establish confirm message, the SEC at 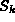 updates the blocking guard
updates the blocking guard 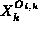 to be
to be 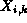 , where
, where
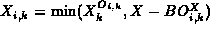 .
The old blocking guard value is stored for use during teardown.
When
.
The old blocking guard value is stored for use during teardown.
When 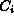 is torn down, the SEC attempts to re-establish the old blocking
guard, as described in Section 4.2.
is torn down, the SEC attempts to re-establish the old blocking
guard, as described in Section 4.2.
The new value for the proposed residual time 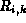 between this and
the next switch is calculated,
between this and
the next switch is calculated,
The new connection is marked as accepted and the establish confirm
message is forwarded to 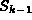 with the updated entries
with the updated entries 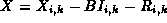 and k-1.
and k-1.
When the establish confirm message reaches the SEC at the
receiver host, the establishment process is completed.



Next: Connection Teardown
Up: The Distributed Admission Control
Previous: The Distributed Admission Control
Riccardo Bettati
Fri Jul 11 18:14:48 CDT 1997