Click on the image to see a PDF version (for zooming in)
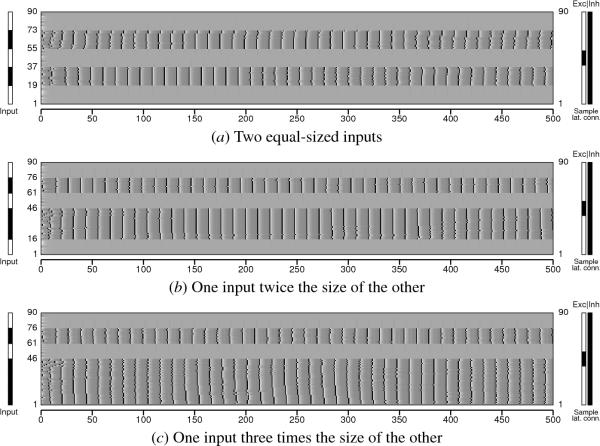
Fig. 12.6. Effect of relative input size on synchronization. A
network of 90 neurons with both excitatory and inhibitory lateral
connections was simulated for 500 iterations. The excitatory
connection radius was 14 and inhibitory connections were global (as
shown at right for neuron 45). The network was given two spatially
separated inputs, and the size of the second input was varied. The
rows (i.e. neurons) that received input are marked by black solid bars
on the left. (a) The two inputs were the same size, activating neurons
[19..36] and [55..72]. (b) One input was twice as long as the
other input, activating neurons [16..45] vs. [61..75]. (c) One
input was three times as long as the other input, activating neurons
[1..45] vs. [61..75]. In all cases, the inputs are robustly bound
and segmented, showing that the behavior is not affected by variation
in the size of the input.
|