CSCE 645/VIZA 675: Geometric Modeling
Assignment 4: Surface Simplification [100 points]
Due 12/2
Purpose:
The goal of this assignment is to load a surface and to simplify the surface down to a specified number of polygons. You will learn about modern surface simplification algorithms as well as implement a mesh-traversal data structure.
Description:
To perform surface simplification, you should implement a mesh-traversal data structure (I suggest the half-edge data structure) and an edge-collapse operator for the surface. This edge-collapse should preserve the topology of the surface. To simplify the assignment, we will not be using the distance to adjacent planes error metric discussed in the lecture since degenerate cases make the problem more difficult to solve. Instead, we will use distance to vertices with the derivation below. You should collapse edges in the order dictated by the error function below and place new vertices at the minimum of this error function.
Let 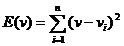 be the error function associated with each vertex of the mesh. If we expand this quadratic, we find that
be the error function associated with each vertex of the mesh. If we expand this quadratic, we find that
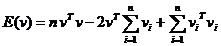 whose minimizer is given by
whose minimizer is given by 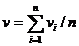 . Therefore, all we need to store to represent this quadratic is
. Therefore, all we need to store to represent this quadratic is 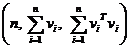 , which is 5 numbers. Furthermore, to create the combined quadratic for the union of two vertices, we simply need to sum the two vectors, each containing 5 numbers, together for the two different vertices.
, which is 5 numbers. Furthermore, to create the combined quadratic for the union of two vertices, we simply need to sum the two vectors, each containing 5 numbers, together for the two different vertices.
Your program should take two arguments: the first will be the name of the obj file to simplify and the second should be the desired number of polygons in the simplified surface. THIS INPUT FORMAT IS NOT NEGOTIABLE. You should perform edge-collapse operations using the error function above until you achieve the desired number of polygons or there are no more edges that can be collapsed safely. Your program should display the simplified surface on the screen and allow the user to rotate the surface to see the results. You should display your surfaces lit using OpenGLís lighting functions meaning that you should calculate a normal for each polygon when displaying the surface. Skeleton code is provided here for you to use, though you may create your own. You may assume that all polygons are triangles and that the input surface is closed. Make sure that your code compiles under Visual Studio in Windows as that's what I'll be using to grade your assignment. INCLUDE AN EXECUTABLE FILE AND ALL DLLS NEEDED TO RUN YOUR PROGRAM WITH YOU ASSIGNMENT. I strongly suggest you implement one of the two optimizations in class (lazy removal or log(n) deletion of arbitrary elements in a heap) for this assignment. I will only allow your code to run for a maximum of 5 minutes on any surface.
We will be using a simplified form of obj file for this project. The file is a text-based, format where each line either starts with a
- "#": a comment meaning that the rest of the line should be ignored,
- "v": a vertex followed by 3 floats (separated by spaces) indicating the x, y, z positions of that vertex. These vertices are considered ordered and have an index equal to the order in which they appear... starting at 1.
- "f": a face followed by 3 positive integers (separated by spaces) indicating the indices of this face from the vertex list
Example surfaces can be found here: big_guy, teeth, happy.
Grading:
[10] Correctly loading the OBJ file and displaying the object
[80] Correct simplification with topology control
[10] Finishing in under 30 seconds.
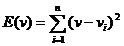 be the error function associated with each vertex of the mesh. If we expand this quadratic, we find that
be the error function associated with each vertex of the mesh. If we expand this quadratic, we find that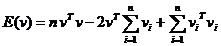 whose minimizer is given by
whose minimizer is given by 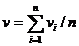 . Therefore, all we need to store to represent this quadratic is
. Therefore, all we need to store to represent this quadratic is 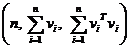 , which is 5 numbers. Furthermore, to create the combined quadratic for the union of two vertices, we simply need to sum the two vectors, each containing 5 numbers, together for the two different vertices.
, which is 5 numbers. Furthermore, to create the combined quadratic for the union of two vertices, we simply need to sum the two vectors, each containing 5 numbers, together for the two different vertices.